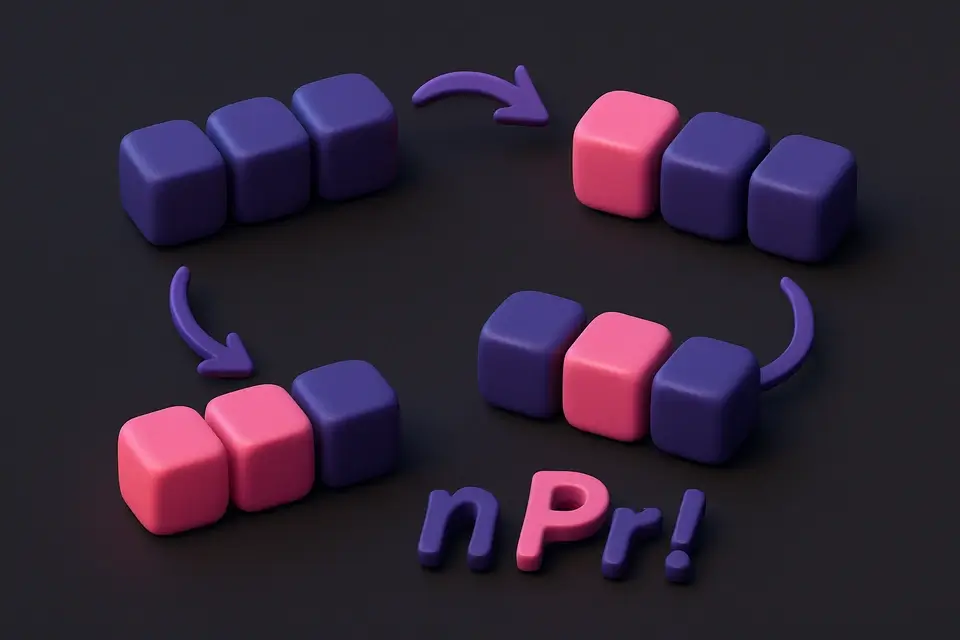
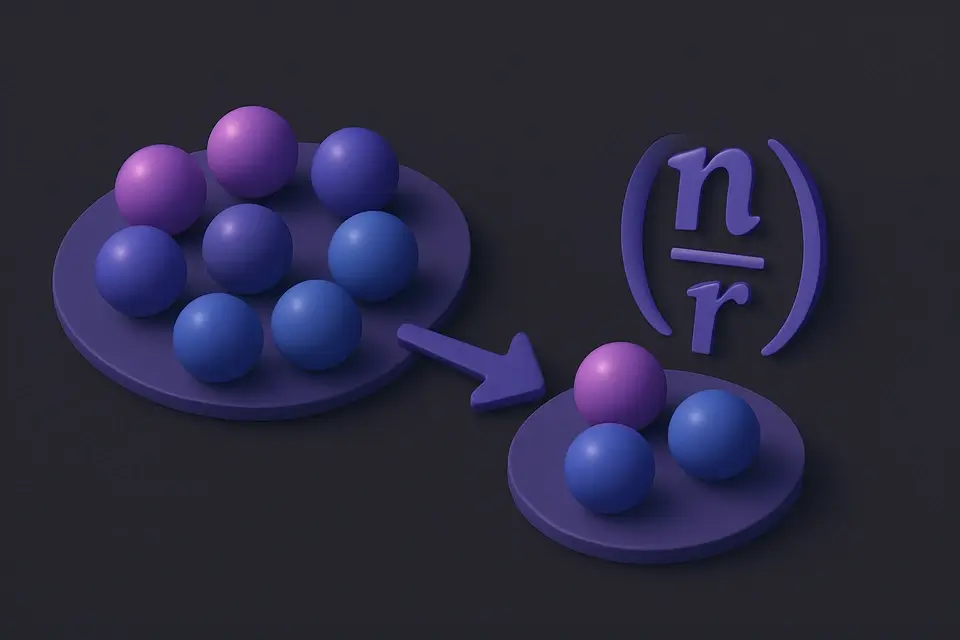
Permutation Calculator (nPr) Calculate the number of permutations (ordered arrangements) of n items taken r at a time.
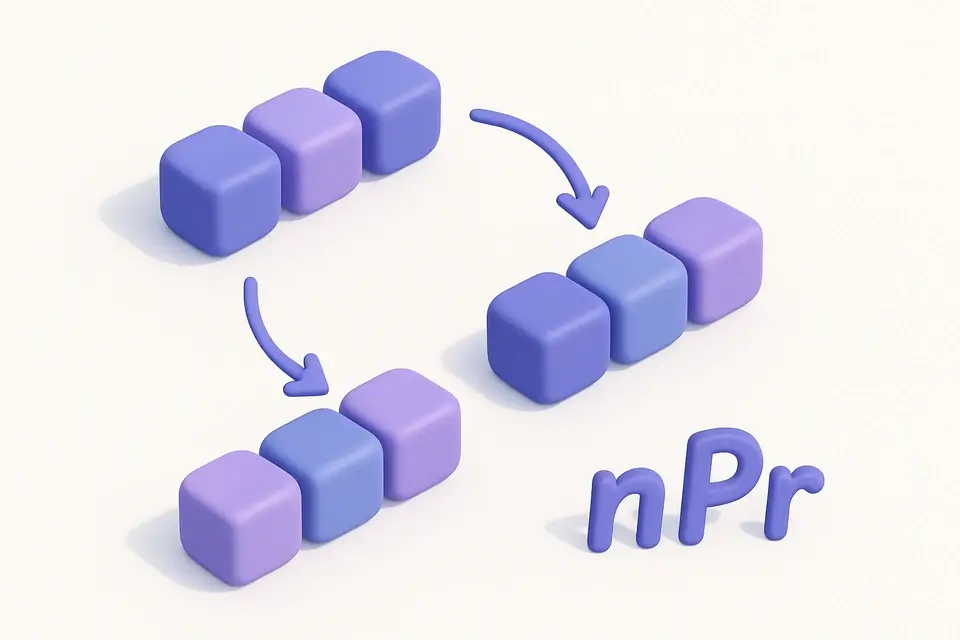
Permutation Calculator (nPr)
Calculate the number of permutations (ordered arrangements) of n items taken r at a time.
Enter n
Input the total number of items available.
Enter r
Input the number of items to arrange (must be ≤ n).
View Result
See P(n,r) calculated with the formula and step-by-step breakdown.
What Is Permutation Calculator (nPr)?
A permutation is an ordered arrangement of items selected from a set. The number of permutations of r items chosen from n items is denoted P(n,r) or nPr, calculated as n!/(n−r)!. Unlike combinations, permutations consider the order of selection — ABC is different from BAC. For example, if you have 10 runners and want to know how many different podium finishes (gold, silver, bronze) are possible, that's P(10,3) = 10!/(10−3)! = 10 × 9 × 8 = 720. Permutations are used in probability, cryptography, password analysis, tournament brackets, and any scenario where the order of selection matters. This calculator uses BigInt arithmetic to handle large values exactly.
Why Use Permutation Calculator (nPr)?
-
Exact BigInt computation for large values
-
Shows the formula and calculation breakdown
-
Handles n up to 1000
-
Clear distinction from combinations (order matters)
-
Instant results for any valid n and r
Common Use Cases
Probability Problems
Calculate the number of favorable ordered outcomes for probability computations.
Password Analysis
Determine the total number of possible passwords of a given length from a character set.
Race Outcomes
Calculate how many different finish orderings are possible for a group of competitors.
Seat Arrangements
Find the number of ways to arrange people in specific seats.
Technical Guide
The permutation formula P(n,r) = n!/(n−r)! counts the number of ways to arrange r items from a set of n, where order matters. This can be computed as n × (n−1) × (n−2) × ... × (n−r+1), which is a falling product of r terms starting from n. The computation uses BigInt to avoid overflow for large factorials. Key identities: P(n,n) = n! (arrange all items), P(n,1) = n (choose one item), P(n,0) = 1 (one way to arrange nothing). The relationship to combinations is P(n,r) = C(n,r) × r!, because each combination can be arranged in r! ways. The number of permutations grows very rapidly with both n and r.
Tips & Best Practices
-
1Remember: permutations care about ORDER (unlike combinations)
-
2P(n,r) = n × (n-1) × ... × (n-r+1) — a falling product of r terms
-
3P(n,n) = n! — arrange all items in every possible order
-
4If r > n, the result is 0 — you can't arrange more items than you have
-
5For permutations with repetition, use n^r instead
Related Tools

Factorial Calculator
Calculate the factorial of any number (n!) with digit count and expansion.
🔢 Math & Calculators
Probability Calculator
Calculate simple probability, union, intersection, conditional probability, and complement.
🔢 Math & Calculators
Combination Calculator (nCr)
Calculate combinations (unordered selections) with or without repetition.
🔢 Math & Calculators
GCD & LCM Calculator
Find the Greatest Common Divisor and Least Common Multiple of two or more numbers.
🔢 Math & CalculatorsFrequently Asked Questions
Q What is the difference between permutations and combinations?
Q When should I use permutations?
Q What if r equals n?
Q What about permutations with repetition?
Q How large can n be?
About This Tool
Permutation Calculator (nPr) is a free online tool by FreeToolkit.ai. All processing happens directly in your browser — your data never leaves your device. No registration or installation required.