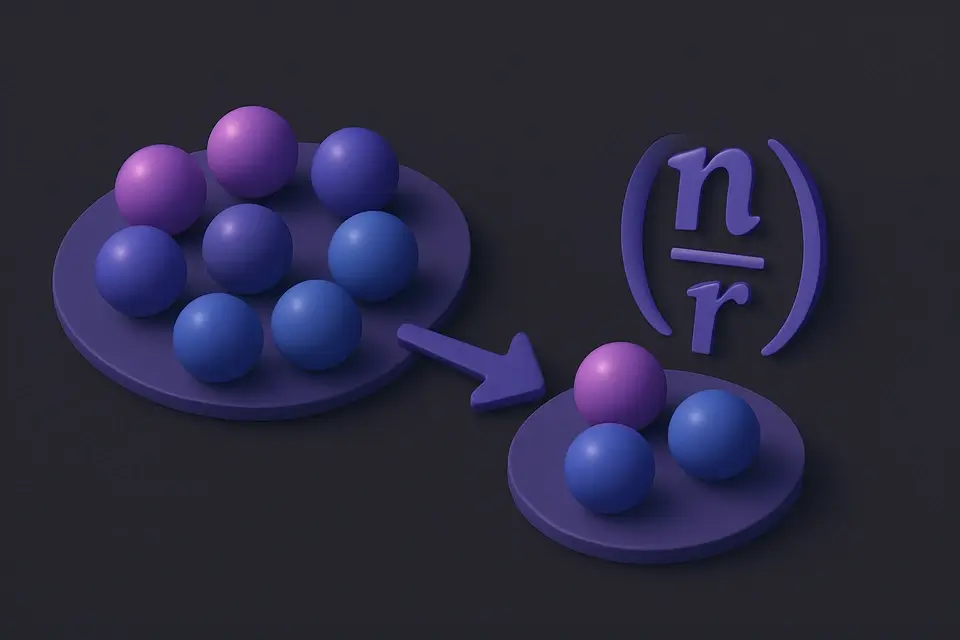
Combination Calculator (nCr) Calculate combinations (unordered selections) with or without repetition.
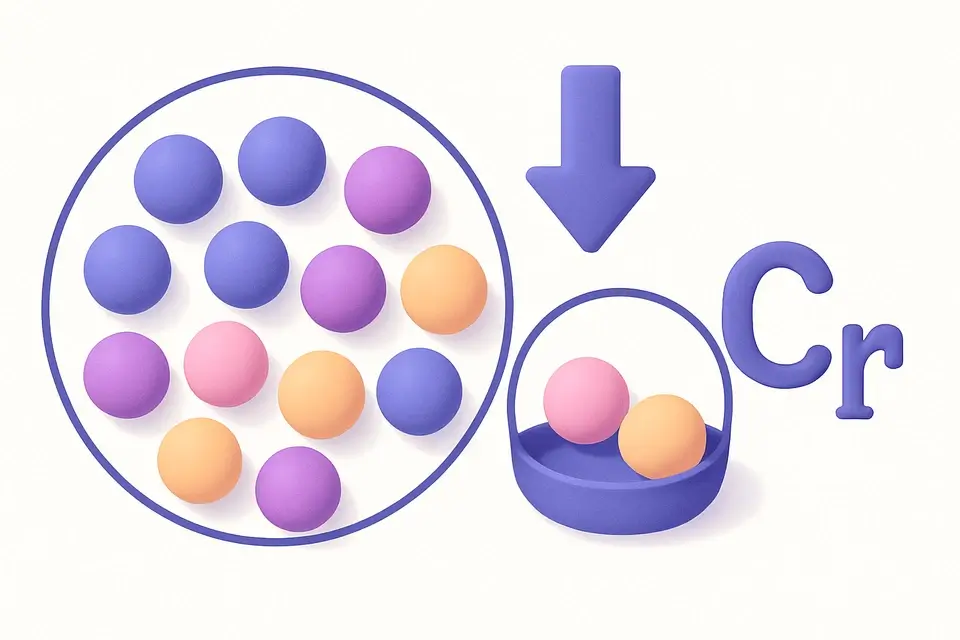
Combination Calculator (nCr)
Calculate combinations (unordered selections) with or without repetition.
Enter n and r
Input the total items (n) and items to choose (r).
Toggle Repetition
Enable "Allow repetition" if items can be chosen more than once.
View Result
See C(n,r) with interpretation of what the number means.
What Is Combination Calculator (nCr)?
A combination is an unordered selection of items from a larger set. C(n,r), also written as "n choose r" or the binomial coefficient (n r), equals n!/(r!(n−r)!). Unlike permutations, combinations do not consider order — selecting ABC is the same as selecting BAC. This concept answers questions like "how many ways can I choose 3 books from a shelf of 10?" — C(10,3) = 120. The calculator also supports combinations with repetition (multichoose), using the formula C(n+r−1, r), for scenarios where items can be selected multiple times. Binomial coefficients appear in Pascal's triangle, the binomial theorem, probability distributions, and combinatorial identities throughout mathematics.
Why Use Combination Calculator (nCr)?
-
Calculates both standard and with-repetition combinations
-
Uses BigInt for exact results with large inputs
-
Shows clear interpretation of what the result means
-
Distinguishes from permutations to avoid common confusion
-
Supports n up to 1000
Common Use Cases
Lottery Odds
Calculate the odds of winning by finding C(n,r) for lottery number selections.
Committee Formation
Find how many ways to form a committee of r people from n candidates.
Menu Combinations
Calculate how many meal combinations are possible from a set of options.
Sampling
Determine the number of possible samples in statistical sampling without replacement.
Technical Guide
The combination formula C(n,r) = n!/(r!(n−r)!) counts unordered selections. It equals P(n,r)/r! since each combination corresponds to r! permutations. Key properties: C(n,0) = C(n,n) = 1, C(n,r) = C(n, n−r) (symmetry), and Pascal's rule: C(n,r) = C(n−1,r−1) + C(n−1,r). Combinations with repetition use the "stars and bars" formula: C(n+r−1, r), which counts the ways to place r identical balls into n distinct boxes. The binomial theorem states (a+b)^n = Σ C(n,k) × a^(n-k) × b^k for k from 0 to n, making binomial coefficients the expansion coefficients. This calculator uses BigInt division of factorials for exact computation.
Tips & Best Practices
-
1C(n,r) = C(n, n-r) — choosing what to include is equivalent to choosing what to exclude
-
2Combinations are always fewer than or equal to permutations for the same n,r
-
3C(n,2) = n(n-1)/2 — a useful shortcut for choosing pairs
-
4Use combinations with repetition when items can be selected multiple times
-
5The sum of all C(n,k) for k=0 to n equals 2^n
Related Tools

Factorial Calculator
Calculate the factorial of any number (n!) with digit count and expansion.
🔢 Math & Calculators
Probability Calculator
Calculate simple probability, union, intersection, conditional probability, and complement.
🔢 Math & Calculators
Permutation Calculator (nPr)
Calculate the number of permutations (ordered arrangements) of n items taken r at a time.
🔢 Math & Calculators
Mortgage Calculator
Calculate monthly mortgage payments, total interest, and view amortization schedule.
🔢 Math & CalculatorsFrequently Asked Questions
Q What is the difference between combinations and permutations?
Q What is "n choose r"?
Q What are combinations with repetition?
Q Why is C(n,0) = 1?
Q How are combinations related to Pascal's triangle?
About This Tool
Combination Calculator (nCr) is a free online tool by FreeToolkit.ai. All processing happens directly in your browser — your data never leaves your device. No registration or installation required.