Trigonometry Calculator Calculate all six trig functions (sin, cos, tan, csc, sec, cot) and inverse trig functions.
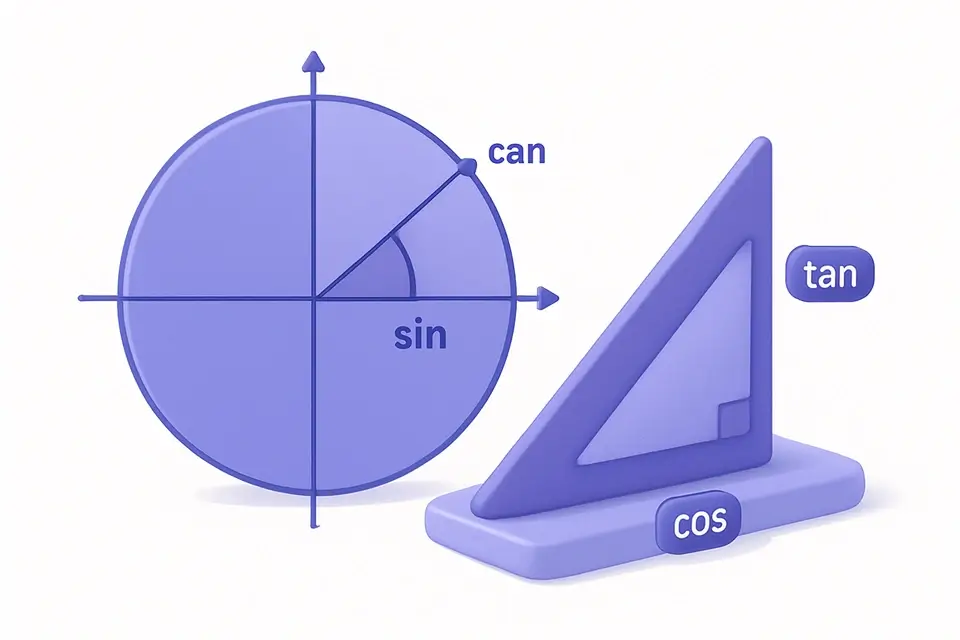
Trigonometry Calculator
Calculate all six trig functions (sin, cos, tan, csc, sec, cot) and inverse trig functions.
Choose Mode
Select forward (angle→values) or inverse (value→angle).
Enter Input
Input an angle (degrees/radians) or a trigonometric value.
View Results
See all six trig functions or the resulting angle.
What Is Trigonometry Calculator?
The Trigonometry Calculator computes all six trigonometric functions for any angle, or finds angles from trigonometric values using inverse functions. In forward mode, enter an angle in degrees or radians to see sin, cos, tan, csc, sec, and cot values. Quick-select buttons for common angles (0°, 30°, 45°, 60°, 90°, 180°) make it easy to reference standard values. In inverse mode, select arcsin, arccos, or arctan, enter a value, and get the angle in both degrees and radians.
Why Use Trigonometry Calculator?
-
All six trig functions calculated simultaneously
-
Both degrees and radians supported
-
Inverse trig functions (arcsin, arccos, arctan)
-
Quick-select buttons for common reference angles
Common Use Cases
Math Homework
Calculate trig function values for geometry and calculus problems.
Engineering
Compute angles and distances for structural and mechanical design.
Physics
Solve wave, rotation, and vector decomposition problems.
Navigation
Calculate bearings, distances, and positions using trigonometry.
Technical Guide
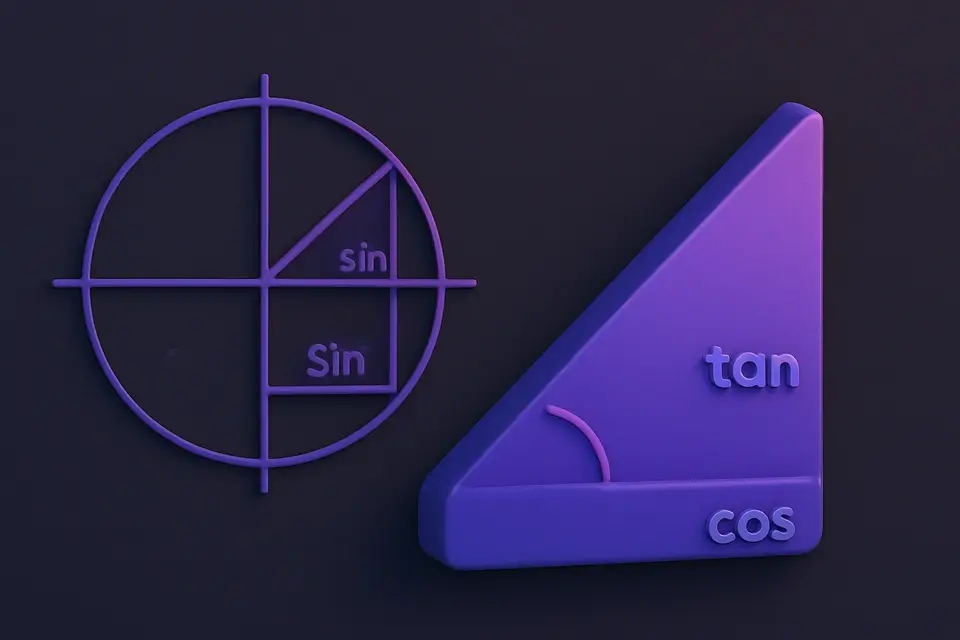
The six trigonometric functions of angle θ: sin(θ) = opposite/hypotenuse, cos(θ) = adjacent/hypotenuse, tan(θ) = sin/cos = opposite/adjacent. Reciprocals: csc(θ) = 1/sin(θ), sec(θ) = 1/cos(θ), cot(θ) = 1/tan(θ). Conversion: radians = degrees × π/180. Inverse functions return angles: arcsin(x) = θ where sin(θ) = x (domain: -1 ≤ x ≤ 1, range: -π/2 to π/2). Undefined values: tan(90°) is undefined (cos = 0), csc(0°) is undefined (sin = 0). The Pythagorean identity: sin²(θ) + cos²(θ) = 1.
Tips & Best Practices
-
1Remember: sin(30°) = 0.5, cos(60°) = 0.5, tan(45°) = 1
-
2Radians are the natural unit in calculus; degrees are more intuitive for everyday use
-
3π radians = 180°, so π/6 = 30°, π/4 = 45°, π/3 = 60°
-
4Values near 0 or ±1 for sin/cos can indicate special angles (0°, 30°, 45°, 60°, 90°)
Related Tools

Scientific Calculator
Full-featured scientific calculator with trigonometry, logarithms, factorials, and more.
🔢 Math & Calculators
Logarithm Calculator
Calculate logarithms in any base (natural log, log₁₀, log₂, custom) and antilogarithms.
🔢 Math & Calculators
Area Calculator
Calculate area and perimeter for 8 shapes — rectangle, circle, triangle, trapezoid, and more.
🔢 Math & Calculators
Percentage Calculator
Calculate percentages, percentage change, and what percent one number is of another.
🔢 Math & CalculatorsFrequently Asked Questions
Q What is the difference between degrees and radians?
Q Why is tan(90°) undefined?
Q What are the domains of inverse trig functions?
Q What is SOH-CAH-TOA?
Q Can I use trig functions for non-right triangles?
About This Tool
Trigonometry Calculator is a free online tool by FreeToolkit.ai. All processing happens directly in your browser — your data never leaves your device. No registration or installation required.