Verify JWT Signatures Online Validate JWT tokens — verify HMAC signature, check expiration, inspect claims.

JWT Validator
Validate JWT tokens — verify HMAC signature, check expiration, inspect claims.
Paste Token
Paste JWT to validate.
Enter Secret
Enter HMAC secret for signature check.
View Results
Check signature and expiry.
What Is JWT Validator?
A JWT Validator is a tool that verifies the authenticity of JSON Web Tokens by checking their digital signatures and ensuring they have not expired. Developers responsible for authentication and authorization use it to identify issues with token validation, such as incorrect signing secrets or expired tokens. One specific problem it solves is verifying the integrity of a JWT when debugging auth issues, allowing developers to pinpoint whether the issue lies in the token itself or elsewhere in their system.
The tool decodes the header and payload of a JWT, checks the expiration claim, and recomputes the HMAC signature for comparison with the provided secret. It supports HS256, HS384, and HS512 algorithms via the Web Crypto API, making it suitable for a variety of use cases that require jwt signature check or to validate jwt token integrity. By pasting a JWT into the tool and providing the signing secret, developers can verify the token's authenticity.
What makes this tool different is its ability to perform these checks entirely client-side, without sending sensitive information like the signing secret to a server. It also provides detailed feedback on the validation result, including whether the signature is valid or not, and whether the token has expired, making it an effective jwt verifier for debugging purposes. If no secret is provided, the tool will still check the structure of the JWT and verify its expiration, providing some level of verification even without the signing key.
Why Use JWT Validator?
-
Verifies HMAC signatures (HS256/384/512)
-
Checks expiration automatically
-
Decodes and displays all claims
-
100% client-side — secrets never transmitted
Common Use Cases
Security Audit
Verify JWT integrity.
Debugging
Diagnose auth failures.
Testing
Verify app-generated tokens.
Compliance
Ensure token security.
Technical Guide
The tool works by first splitting the input JWT into its three constituent parts using the `split()` method with a period as the separator. It then decodes the header and payload sections from base64url format to JSON objects using the `atob()` function in conjunction with string replacement operations to handle the differences between base64 and base64url encodings. The decoded header is used to determine the algorithm employed for signing, which is then looked up in a mapping object `aMap` that associates standard HMAC algorithm names like HS256, HS384, and HS512 with their corresponding hash functions from the SHA-2 family, such as SHA-256, SHA-384, and SHA-512.
When a secret is provided, it recomputes the HMAC signature over the concatenated header and payload using the Web Crypto API's `crypto.subtle.sign()` function in conjunction with an imported key derived from the secret via `crypto.subtle.importKey()`. This recompute operation allows for comparison of the generated signature with the one included in the JWT to verify its authenticity. Additionally, it checks if the token has expired by comparing the expiration time claim (`exp`) in the payload against the current system time obtained through `Date.now()`, providing a clear indication of whether the token is still valid or not. The tool utilizes React state management mechanisms like `useState` and event handling callbacks defined with `useCallback` to manage user input, validation results, and any error messages that may arise during the validation process.
The use of specific technologies such as React for building the interface, TypeScript for type safety, and the Web Crypto API for cryptographic operations ensures a secure and reliable validation experience. The support for multiple HMAC algorithms through the `aMap` object makes it adaptable to different security requirements. By performing these checks entirely on the client side without requiring server-side communication, the tool maintains the confidentiality of sensitive information like signing secrets, enhancing its utility in debugging authentication issues where token integrity is paramount.
Tips & Best Practices
-
1Use HMAC algorithms like HS256, HS384, or HS512 for signature verification as defined in the aMap object
-
2Trim the JWT token before validating to prevent errors from whitespace characters
-
3Check the payload's exp claim to determine if the token has expired
-
4Verify the signature by comparing it with the expected value calculated using the secret and algorithm
-
5Decode Base64Url-encoded strings using the decB64Url function
-
6Handle validation errors by checking the err state variable for messages like 'Invalid JWT' or 'Failed to decode JWT'
Related Tools
SHA-256 Hash Generator
Generate SHA-256 hash digests.
🔐 Encoding & Crypto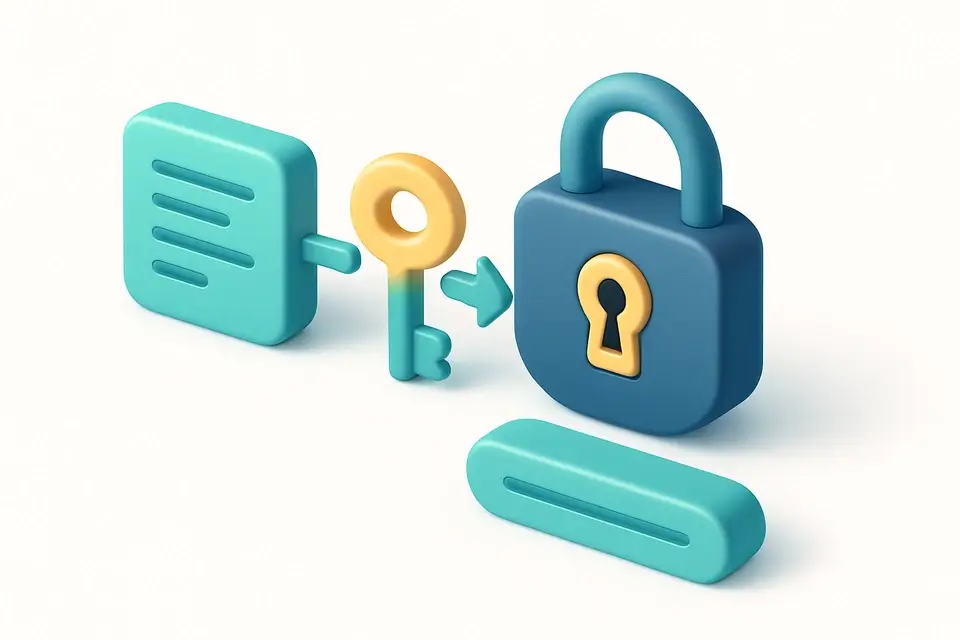
HMAC Generator
Generate HMAC digests with multiple hash algorithms.
🔐 Encoding & Crypto
JWT Decoder
Decode and inspect JSON Web Tokens — view header, payload, and expiration status.
🔐 Encoding & Crypto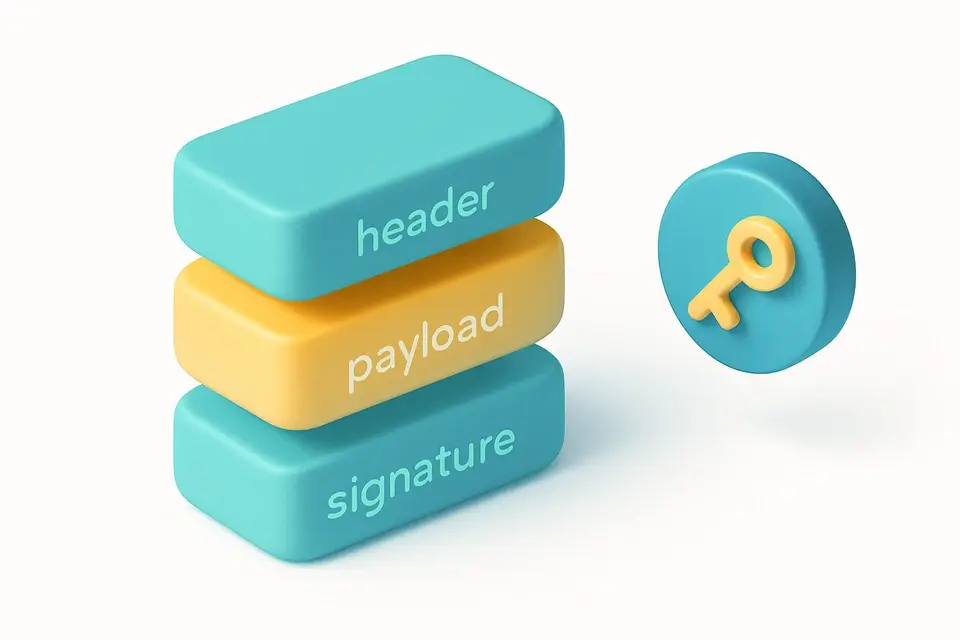
JWT Generator
Generate signed JSON Web Tokens with custom claims, algorithm selection, and expiration.
🔐 Encoding & CryptoFrequently Asked Questions
Q Is the JWT validator free?
Q Is my secret safe when validating JWTs?
Q What can I validate without the secret?
Q Which signing algorithms are supported?
Q Does it detect expired tokens?
About This Tool
JWT Validator is a free online tool by FreeToolkit.ai. All processing happens directly in your browser — your data never leaves your device. No registration or installation required.




