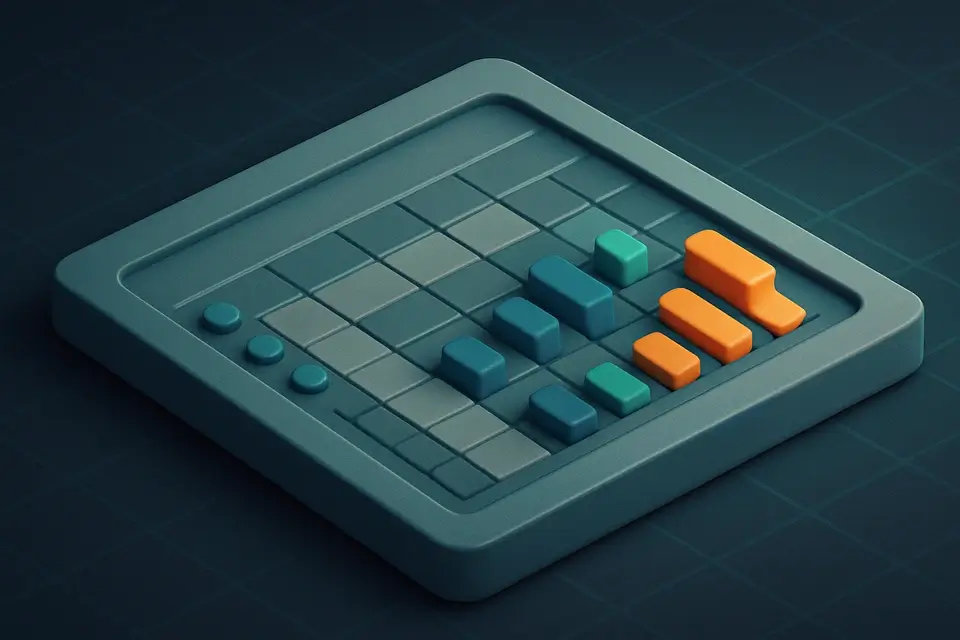
Weighted Decision Matrix Weighted decision matrix for comparing options across multiple criteria with scoring.

Decision Matrix
Weighted decision matrix for comparing options across multiple criteria with scoring.
Define Criteria Weights
Assign weights to each criterion by adjusting the range input, with values between 1 and 10. This step is crucial as it determines the importance of each criterion in the decision-making process.
Score Options Against Criteria
Fill in the scores for each option against each criterion, using a scale of 0 to 10. These scores will be used to calculate the weighted totals for each option.
Evaluate Weighted Totals
Compare the weighted totals for each option, which are calculated by multiplying the score for each criterion by its corresponding weight and summing these products. The option with the highest total is considered the winner.
What Is Decision Matrix?
A Decision Matrix is a decision making tool that evaluates options against multiple criteria by calculating weighted scores, which are the sum of weight multiplied by score per criterion. This technique is commonly used by product managers, engineers, and business analysts to make informed decisions when faced with complex choices. One specific problem it solves is comparing multiple alternatives with different strengths and weaknesses, such as evaluating features for a new product release.
The tool is particularly useful in situations where there are conflicting priorities, and a weighted decision matrix helps to quantify the importance of each criterion. For instance, when deciding between two software development frameworks, criteria like performance, scalability, and maintenance cost can be assigned different weights based on their relative importance. It allows users to add or remove options and criteria as needed, making it adaptable to various comparison matrix scenarios, including Pugh Matrix analysis.
What makes this tool different is its interactive table with editable cells, where users can input scores for each option against each criterion, and the weighted scores are automatically calculated and ranked. The automatic ranking feature provides a clear visualization of the results, highlighting the top-scoring options, which can be further refined by adjusting the weights or scores in the comparison matrix. Additionally, it includes features like adding or removing criteria, and editing their weights using a range input, allowing for fine-grained control over the decision-making process.
Why Use Decision Matrix?
-
Instant weighted scoring with automatic ranking
-
Runs entirely in your browser — your data stays private
-
No signup or installation required
-
Mobile-friendly responsive interface
Common Use Cases
Evaluating Business Partnerships
As a CEO, Sarah uses weighted criteria like financial stability and shared values to compare potential partners. She scores each option from 1 to 10 based on these factors. This process helps her identify the most suitable partner for her company's expansion plans.
Comparing Investment Opportunities
Investor Michael analyzes different assets by assigning weights to criteria such as risk level and potential return. He then calculates a weighted total for each option, allowing him to visualize which investments are likely to yield the best results.
Selecting Project Management Tools
Project manager Emily creates a list of key features she needs in a tool, including task tracking and team collaboration. She evaluates several tools against these criteria, scoring each one based on how well it meets her requirements.
Choosing a Cloud Hosting Service
Developer David considers factors like scalability, security, and cost when evaluating cloud hosting services. By using a systematic approach to compare options, he can ensure his application's infrastructure is reliable and efficient.
Prioritizing Product Features
Product owner Rachel identifies the most important features for her product's next release by weighing customer demand against development time and resource constraints. This helps her prioritize which features to implement first, maximizing the impact on user satisfaction and revenue growth.
Optimizing Supply Chain Logistics
Logistics manager Tom assesses different shipping routes and carriers based on criteria like transit time, cost, and reliability. He calculates a weighted score for each option, enabling him to select the most efficient and cost-effective logistics strategy for his company's supply chain.
Technical Guide
The tool uses React's useState hook to store options, criteria, and scores in memory, with each option and criterion represented as a JavaScript object. The scores are stored as a record of strings to numbers, where the key is a concatenation of the option ID and criterion ID. When a user inputs a score or edits an option or criterion name, the corresponding state is updated using callbacks like setScore, addOption, or addCriterion. These updates trigger React's virtual DOM to re-render the table with the new data.
Under the hood, the tool relies on JavaScript's built-in array methods like map and reduce to calculate the weighted scores for each option. The totals are computed by iterating over each criterion, multiplying its weight by the score for that criterion, and summing up these products. This process is repeated for all options, resulting in an array of objects with the total weighted score for each option. The maxTotal is then calculated as the maximum of these totals, which is used to determine the winner and visualize the results.
The tool also uses React's useMemo hook to memoize the calculation of the totals and maxPossible values, ensuring that they are only re-computed when the dependencies change. This optimization improves performance by avoiding unnecessary recalculations. Additionally, the code utilizes TypeScript to define interfaces for options and criteria, providing type safety and helping catch errors at compile-time rather than runtime.
The automatic ranking feature is implemented using JavaScript's sort method, which sorts the totals array in descending order based on the total weighted score. The winner is then determined as the option with the highest total score, and its ID is stored in the winnerId variable. The results visualization uses a combination of HTML and CSS to display the ranked options, with the top-scoring option highlighted in green.
Tips & Best Practices
-
1Set weights for each criterion to prioritize them
-
2Assign scores based on option performance against each criterion
-
3Remove options that are clearly inferior to narrow down choices
-
4Adjust weights and scores iteratively to refine the decision
-
5Use the weighted total row to compare options side-by-side
Related Tools

Email Validator
Validate email addresses against RFC 5322 format rules with detailed error explanations.
🧰 Miscellaneous
Credit Card Validator
Validate credit card numbers using the Luhn algorithm with card network detection.
🧰 Miscellaneous
URL Validator
Validate URL format and structure with protocol, domain, path, and query string analysis.
🧰 Miscellaneous
JSON Validator
Validate JSON syntax with detailed error messages showing the exact location of issues.
🧰 MiscellaneousFrequently Asked Questions
Q Is this decision matrix tool free to use?
Q Is my data safe in this online decision matrix?
Q Can I use the decision matrix on my phone?
Q How are the weighted scores calculated?
About This Tool
Decision Matrix is a free online tool by FreeToolkit.ai. All processing happens directly in your browser — your data never leaves your device. No registration or installation required.




