CSV to SQL INSERT Converter Generate SQL INSERT statements from CSV data with automatic type detection.
CSV to SQL
Generate SQL INSERT statements from CSV data with automatic type detection.
Paste CSV data
Paste your CSV with headers. Set the target table name.
Auto-generate SQL
INSERT statements are generated automatically for each row.
Copy the SQL and run in your database
Copy the SQL statements and run them in your database.
What Is CSV to SQL?
CSV to SQL generates SQL INSERT statements from comma-separated data. This tool takes your CSV input, uses the header row for column names, and creates properly formatted INSERT statements for each data row. It automatically detects numeric values (outputting them without quotes) and handles NULL values, empty strings, and SQL injection-safe string escaping. The table name is customizable to match your database schema. This is invaluable for database seeding, data migration, and quick data imports.
Why Use CSV to SQL?
-
Automatic type detection: numbers output without quotes, strings properly escaped.
-
Customizable table name to match your database schema.
-
SQL injection-safe string escaping with single-quote doubling.
-
Handles NULL values and empty fields appropriately.
Common Use Cases
Database Seeding
Generate INSERT statements from seed data in spreadsheets for database initialization.
Data Migration
Convert CSV data exports into SQL for import into relational databases.
Testing
Create test data INSERT statements from CSV test fixtures.
Quick Data Import
Import spreadsheet data into MySQL, PostgreSQL, or SQLite without ETL tools.
Technical Guide
The converter generates standard SQL INSERT statements compatible with MySQL, PostgreSQL, SQLite, and most SQL databases. Column names from the CSV header are wrapped in backticks for compatibility with reserved words.
Type detection works as follows: values matching the pattern of integers or decimals (including negative numbers) are output without quotes as numeric literals. Values equal to "null" (case-insensitive) or empty strings are output as SQL NULL. All other values are treated as strings, wrapped in single quotes, with any internal single quotes escaped by doubling them.
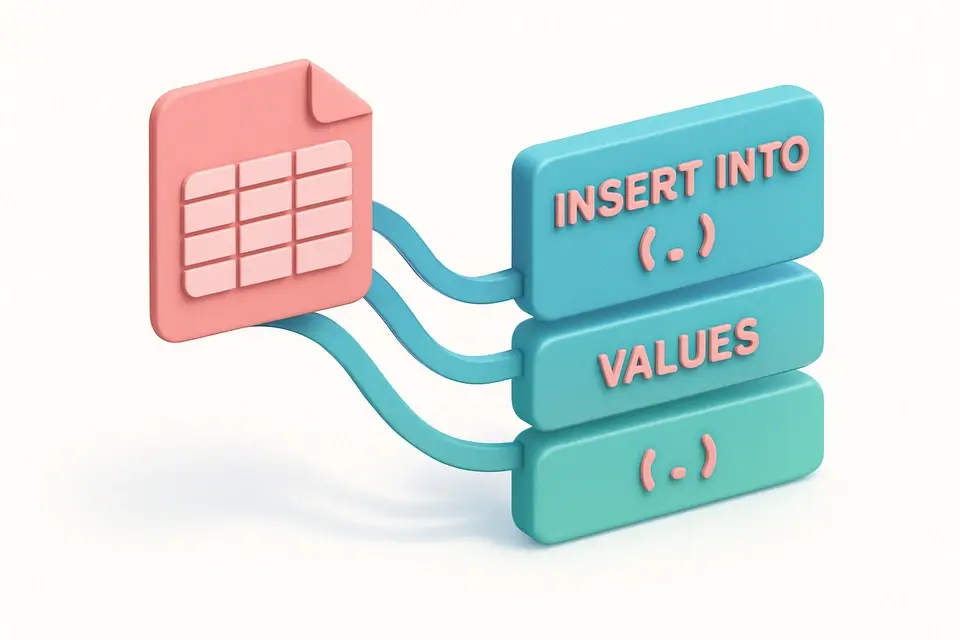
Each INSERT statement follows the format: INSERT INTO `table` (`col1`, `col2`) VALUES (value1, value2); This format is widely compatible across SQL dialects.
For large datasets, consider wrapping the output in a transaction (BEGIN; ... COMMIT;) for better performance.
Tips & Best Practices
-
1Set a meaningful table name that matches your database schema before generating.
-
2Numeric values are auto-detected — ensure numbers in your CSV don't have formatting (commas, currency symbols).
-
3Empty values and "null" text are converted to SQL NULL.
-
4For large imports, wrap the output in BEGIN; ... COMMIT; for better database performance.
Related Tools
CSV to JSON
Convert CSV data to JSON array format instantly in your browser.
🔄 File Conversion
CSV to XML
Convert CSV data to well-formed XML with customizable root and row tags.
🔄 File Conversion
SQL to CSV
Extract data from SQL INSERT statements and convert to CSV format.
🔄 File Conversion
JSON to SQL Schema
Generate CREATE TABLE SQL statements from JSON data with type inference.
🔄 File ConversionFrequently Asked Questions
Q What SQL databases are supported?
Q How are NULL values handled?
Q Is the output safe from SQL injection?
Q Can I change the table name?
Q Are numeric values properly handled?
About This Tool
CSV to SQL is a free online tool by FreeToolkit.ai. All processing happens directly in your browser — your data never leaves your device. No registration or installation required.